What You Should Know About the Saudi Code of Sharia Litigation
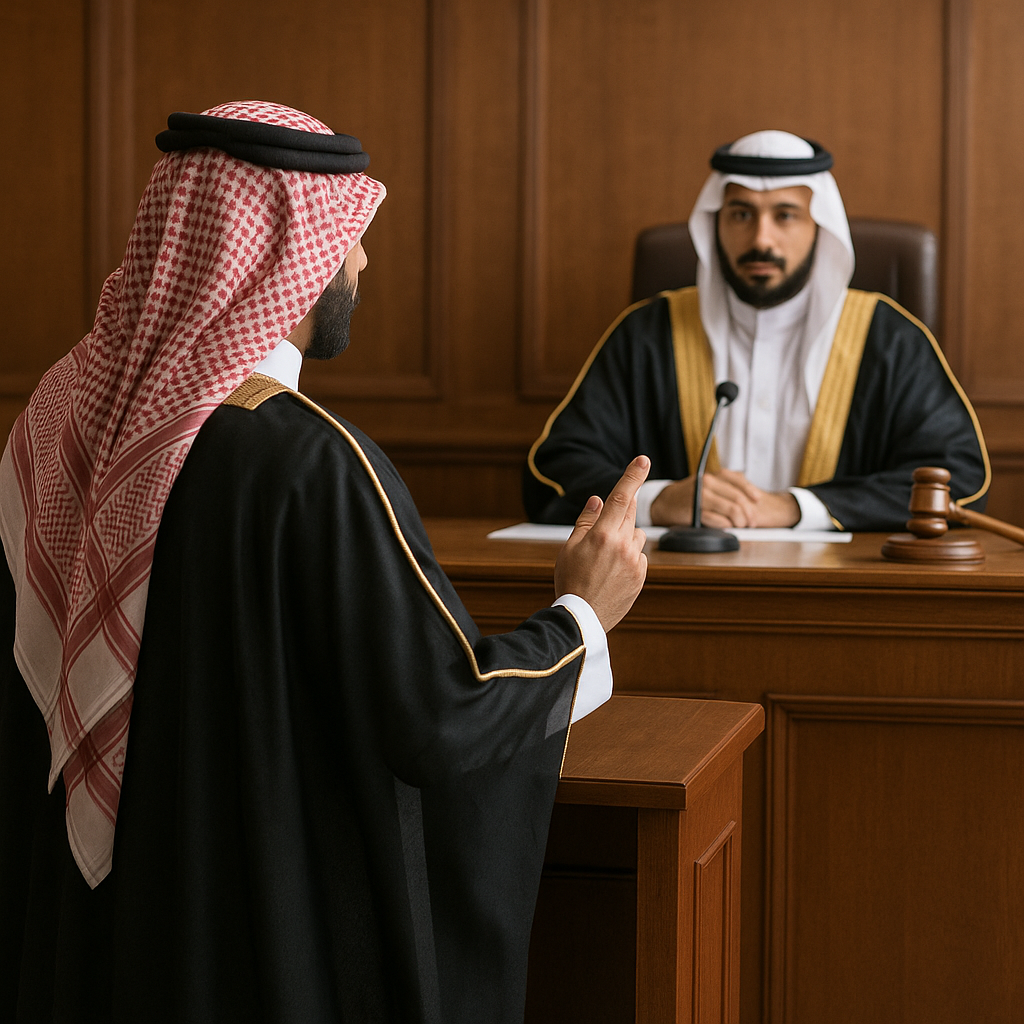

The Saudi Code of Sharia Litigation governs court procedures from filing a lawsuit to issuing and enforcing a judgment. It serves as the primary legal reference for judges, lawyers, plaintiffs, and defendants across the Kingdom’s judicial system.
When Does This Code Apply?
The code applies to all civil and rights-related disputes—such as contracts, debts, real estate, commercial, and family cases—except for criminal matters, which are governed by the Criminal Procedure Law.
Litigation vs. Criminal Procedures: What’s the Difference?
- Sharia litigation: Covers civil, commercial, and personal status cases.
- Criminal procedures: Deal with crimes and public prosecution cases.
How to File a Lawsuit in Saudi Arabia
- Visit the Najiz platform.
- Select “New Lawsuit Filing”.
- Fill in the plaintiff and defendant details and upload the required documents.
- Follow up with electronic notifications and court session scheduling.
Is Hiring a Lawyer Mandatory?
No, but hiring a specialized attorney significantly increases your chances of winning the case and expediting legal procedures, especially in complex matters.
Key Requirements for Accepting a Lawsuit
- A legitimate and direct legal interest must exist.
- The case must be filed against the correct party.
- It must be filed before the statute of limitations expires.
- It must be filed with the court that has proper jurisdiction.
How Long Does the Process Take?
The timeline varies depending on the case type and complexity, but electronic hearings are helping expedite proceedings.
How Is the Defendant Notified?
Through text messages, email, or the “Tawakkalna” app—these are considered official notifications. If the defendant is unreachable, the court may order public notification through newspaper announcements.
Litigation Stages Under the Saudi Legal System
- Filing and registering the case
- Case preparation and notification
- Court hearings and pleadings
- Issuance of the judgment
- Appeal, if applicable
- Enforcement through execution courts
When Is a Judgment Considered Final?
- If no appeal is filed within 30 days of the judgment date.
- If it is issued directly by the appellate court in specific cases.
Can Judgment Enforcement Be Paused?
Yes, the judge may issue a temporary suspension of enforcement if an appeal request is submitted with valid reasoning.
Penalties for Abusing the Legal System or Delaying Cases
- Monetary fines
- Case dismissal due to lack of seriousness
- In some cases, compensation awarded to the affected party
Important Notes:
- Lawsuits without clear evidence or purpose are dismissed.
- Courtroom etiquette is mandatory (respect, no interruptions, proper language).
- Digital evidence such as emails, text messages, and recordings are admissible.
- Urgent cases such as travel bans or rights preservation can be filed through summary proceedings.
Legal Summary:
The Saudi Sharia litigation system is the foundation for ensuring justice in civil and commercial disputes. It gives every party the right to present evidence and defend themselves within a transparent and regulated framework. To protect your legal rights, consider legal consultation or representation when necessary.




Comments